Introduction
The days of limited activity metrics—like attendance, exit surveys, and course count—are over.
Enterprise training has become a sophisticated locus of talent management innovation, driving business success. Among training teams in leading organizations, the accessibility, analysis, and utilization of a well-crafted data architecture fuels and informs this innovation, not only for the training function but for the success of the business as a whole.
In this guide, we’ll discuss the significance of data literacy, as well as the risk of failing to pursue this core skill for training leaders today. We’ll identify three myths about training data management that hold back training teams from realizing their full impact in the organization. And, we’ll outline how to architect your plan for mining decision-ready from the training function, transforming training from a cost center to an intelligence hub for your organization.
Researching how training can enter the decision economy is a powerful first step in putting your training data to work as organizational intelligence. Let’s get started.
“I love learning from and sharing challenges with other CEOs and business leaders. One thing I’ve seen consistently is that training data is often overlooked when attempting to solve key business problems, and this is often a mistake – training data can be some of the best signal a business has and can be used as both a leading and lagging indicator to help solve problems.”
Data Literacy & Training
Why leading enterprise training teams must level up data fluency

Data alone doesn’t drive decisions. Your data-grounded insights do.
Data literacy is a learned skill that provides the ability to interrogate, understand, and communicate effectively with data. It includes critical thinking components that facilitate the analysis of data, and communication skills that make it possible to tell your story using data.
Every business leader today knows that data utilization is important, but the urgency felt by training leaders for adopting this expertise increases when the risks of failing to leverage training data well are considered.
The risks of weak data literacy for training include:
- An inability to demonstrate the ROI for training, leaving budget and key project sponsorship at risk, despite growing demand driven by workforce changes.
- Isolation of training insights, limiting the leverage of this institutional evidence to talent management alone instead of the full scope of business impact.
- Defaulting to reactive training tactics that merely respond to business needs that have already created a pressure on the business rather than formulating proactive strategies that anticipate training needs and the power of learning to increase performance.
The state of data literacy in enterprise
If your organization is just beginning to implement data literacy, you’re not alone. Despite a decades-long focus on data acquisition, Americans rank toward the bottom of a global survey on data literacy. A report from the National Center of Education Statistics (NCES) surveyed the data literacy of working age adults. America ranked 21st out of 23 countries participating.
Despite the fever-pitch focus on the importance of data in business, the needle for data mastery hasn’t moved that much in recent years. A 2020 Forrester report found only 40% of employees feel they have the data skills required for their role. This is despite the fact that the same report shows 82% of leaders expect all employees to have basic data literacy and 70% of employees are expected to heavily use data by 2025, up from 40% in 2018.

Learning technology and training’s struggle for improved data utilization
As has been true in every corner of the enterprise organization, the conversation on data literacy within the training function runs parallel to the evolution of the technology that serves the mission of learning and development.
Perhaps more lagging than other mission critical areas, training has sustained a large gap when it comes to operational technologies and technological investment. This lack of investment has meant a lack of accessibility to collective, coherent data models and the resulting delay of the opportunity to develop data competency among staff.
The data utilization impact gap can be measured in dollars. A 2018 IDC study reveals that enterprise-scale companies invested trillions in key projects aimed to update their business, but 70 percent of these projects have failed because technology investments accelerated without considering data literacy among teams impacted. Commonly, the relentless focus on data acquisition has stranded many enterprise teams, including training, with a wealth of data but meager options to analyze or act upon their findings.
Investing in data literacy is the first step to remedying analysis paralysis. The investment doesn’t need to be huge, a simple change of mindset and willingness to politely interrogate data is a great start.
BREAK IT DOWN
Data literacy shares your impact
A training team that is data literate can:
- Ask the right questions to interrogate your data.
- Understand which data is relevant.
- Conduct tests to prove the validity of the data.
- Interpret data into useful and meaningful results.
- Visualize data to quickly communicate your impact.
- Tell a story with data to engage and convince stakeholders.
BRING IT TOGETHER
Always interrogate your data
Adopting a curiosity about data is the cost of data literacy. Consider these questions, which should be asked as a matter of course.
- How important is this decision?
- Will this decision only serve the training function, or the organization as a whole?
- What data do we have, or can acquire, that supports or challenges this idea?
- Have we tested this result/data? What is required to be confident in this data?
- What further evidence do we need to act on this data?
Data literacy: competitive advantage for Ping Identity
The second largest repository of data for Ping Identity (formerly ForgeRock), one of the leaders in identity management, is their training data. This has become an incredible advantage for the fast growing startup which went public last year. By marrying training data with other operational business metrics, they helped build an early warning system that could detect potential customer churn. By integrating digital badging with their training platform, they generated leads as students shared their learning achievements on social media, interesting others.
“One of the most common problems, when you’re running things manually from spreadsheets, is scaling your operation. The standard response is to expand the team and hire new staff. Actually the answer should be to invest in your system infrastructure. The answer is Administrate.”
Training Data Myths
Eliminating common assumptions that may be blocking data-driven decision making

Training has always collected data, but has seldom driven it.
Always, in defense of tight budgets and limited time, training teams have focused on capturing high-level data on learner and program performance. These descriptive analytics maintain foundational importance when understanding the value of training and the measure of this key organizational investment. While these numbers are important, they are limited in their ability to invoke deeper insights into future needs or immediate opportunities for business wins.
Where analysis of training data does take place, it is frequently dependent upon spreadsheets that require manual effort to maintain but provide little value to the organization. It can be difficult to establish data correlation across training tools themselves, let alone relate to larger organizational KPIs.
Evolving your ability to harness training data will require change. The first change is in your organizational mindset about the data itself. What assumptions or limiting beliefs are present within your organization that are hindering your ability to grow toward data-driven decision making for your program and your organization?
3 common myths about training data
1.
The myth of excess:
“We have a lot of reports already.”
Volume is not the sole determinant of value when it comes to data. If your program is like most, you are using anywhere from nine to 12 disparate systems or software to plan, produce, deliver and report on your training program.
Each of these tools is producing data points. It is easy to get lost in the assumption that you do have the data you need because the tool offered you some numbers. However, if you’re using pre-programmed reports embedded in the tool, chances are that the output is more aligned to the tool’s marketing pitch and value proposition than it is to the impact of your program on your business. Do you have data that actually reports on your program, or data that reports on your tools? There’s a difference.
2.
The myth of access:
“We have a lot of reports already.”

Like many good stories, this myth resonates because there has been some truth in it. Until recently, it has been difficult to imagine a way to create a holistic data architecture and reporting alignment of the training function.
In fact, this need is largely responsible for the emergence of training management platforms, including Administrate. Because training touches knowledge, skill, experience, compliance, and a multitude of intellectual and physical resources, it is imperative that 100% of your training data be accessible and reportable. Now, that access is possible. Achieving this level of access may require you to think differently about creating a learning technology infrastructure for your program—not unlike the similar progression of operations toward ERP systems. If training operations platforms are new to you, take time to learn about the possibilities they offer before you settle for the limitation of included reports.
3.
The myth of isolated impact:
“Training data is primarily about the training program.”
Many organizations have outgrown siloed thinking, but few have operationalized beyond it. With workforce sea changes like “The Great Resignation” and the still resolving question of distributed teams versus hybrid versus in-office work models, never has it been more apparent that the training team is a vital function not only in the sustainability of the entire organization but also in its ability to remain agile and competitive. Expanding that confidence beyond the function of training to training’s data is the crossroads where many leading organizations now find themselves. They know training is strategic, but how do they interrogate that data to mine the beneficial business intelligence that it offers?
Training leaders are embracing this new role of business intelligence and equipping their teams to provide analysis and insights beyond the former up-level reports. They are providing forecasts of business impact based on learner results gathered and connecting this information to production capacity, scheduling, and more. Talent retention strategies include learning and development as a key stakeholder as candidates, many of whom anticipate changing careers three to four times in their lives, value training as a benefit on par with 401k investments and health savings accounts.
Connecting the valuable organizational data that training offers via diagnostic analytics is the first step to dispelling this myth. Once you can show how training impacted specific KPIs throughout the organization, you can demonstrate how training data is relevant for other functions. From there, predictive and prescriptive analytics can be leveraged to shape strategic decisions for talent, production, finance, and more. Breaking training data out of isolation requires adding context to that data.
By dispelling these training data myths you:BREAK IT DOWN
Dispelling data myths gives you influence over strategy
These ideas will help you dispel these myths:BRING IT TOGETHER
Mindset shift and tech investment
A maritime manufacturer reveals organizational value in training data
In eighteen months, a maritime manufacturer needed to double the production of their factory and launch several new boat models, which meant increasing the physical size of their factory and doubling their headcount.
To accomplish this, the entire management team worked together to invest in a training platform that could support a large intake of new employees and train on the construction techniques required for their new boat models. While expanding, they also needed to reduce manufacturing errors and involuntary employee turnover, and by marrying their training data with metrics from their factory production systems, they could pinpoint when and where errors were happening and intervene with timely instruction.
Architect Decision Analysis
Using operational constraints and requirements to accelerate data-driven decision making

Combine training data with operational requirements within a training operations platform to execute data-driven decisions.
Training teams that want to participate in the decision economy need to tell their story through data, connect training data to larger organizational goals, and automate their decision making. Even highly data-fluent teams, equipped with the most reliable information can still fail to make accurate, and repeatable, decisions. Why? Many overlook the secret to decision analysis hiding in plain sight: operational requirements.
Training operations: the root of decision analysis
You may not think the operational requirements that drive your daily training programs are also key to data analysis, but they are the exact inputs that help technology automate many types of decision making for you.
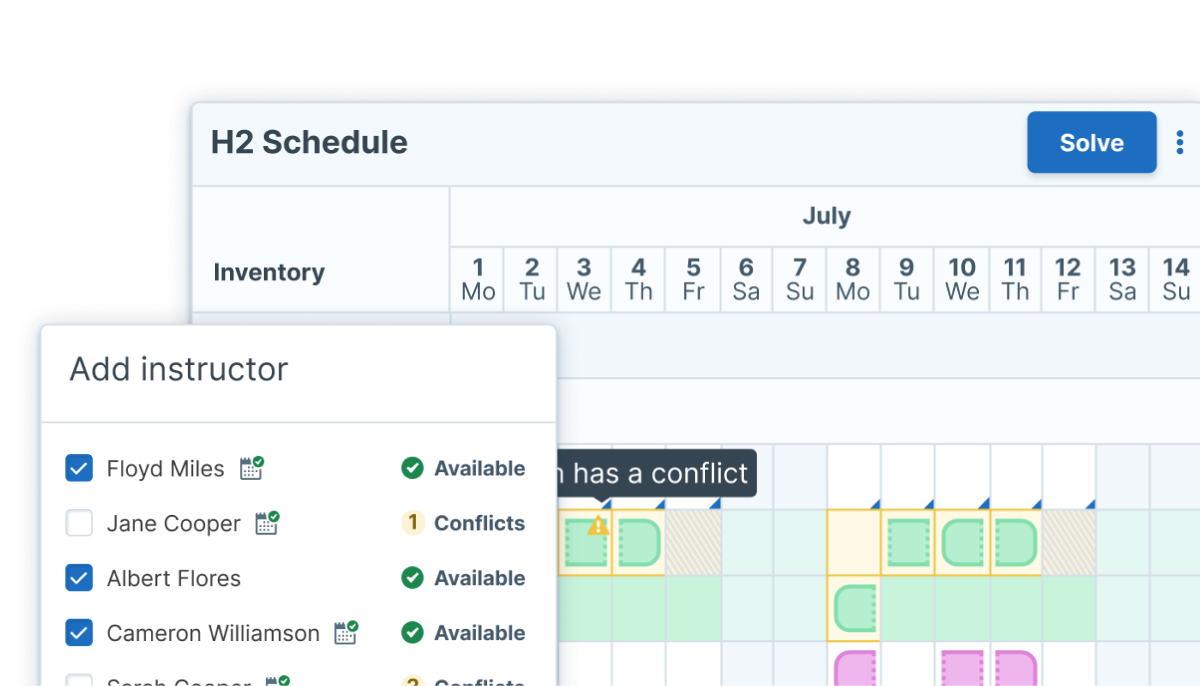
Imagine how a quarterly training event calendar comes together: weeks are spent collecting requirements from across the organization, dozens of calendars are consulted, whiteboards are scribbled with notes about instructors, classrooms, or equipment, and your training team spends late nights hashing out the nuances of conflicting schedules. It takes weeks, maybe a month.
These whiteboard notes and coffee-fueled ideas about resource constraints are inputs that add context to data, and ultimately help automate decisions around complex training logistics.
Scheduling a calendar of events is just one example, your team is deep into these operational quagmires every day. All of them are opportunities for decision analysis.
Identify operational requirements to drive decisions
By tracking operational requirements, you can understand the scaffolding of decision making as a process. For example, by knowing your instructor’s calendars, you can cross reference a classroom calendar and only schedule that instructor into classrooms that are available.
That is a very simplistic decision, not one likely to change your organization, but when you scale such a simple decision across your entire training function, the manual effort this requires becomes a true cost to the enterprise.
Now, layer on more requirements to this simple scenario. What if data reveals this instructor performs well with certain cohorts? What if those cohorts have to meet regulatory requirements for specific training by a certain date, throwing the original training calendar into disarray?
Sure you could train these cohorts using a different set of instructors, but their performance may drop. How do you balance this scenario for the best possible outcomes? With regulatory requirements in play, this seemingly mundane choice could impact the entire organization.
These are all decision-points that contribute to arriving at a final choice
The cost for operationalizing decision making is fairly cheap: these questions interrogate your training operations and reveal requirements to drive decision making. Your team can likely answer these questions very easily.BRING IT TOGETHER
Operational requirements drive decision-making
Investigate a Training Management System for rapid decision-making
Administrate helps enterprise training teams make rapid decisions and simplify logistics by combining training data and operational requirements.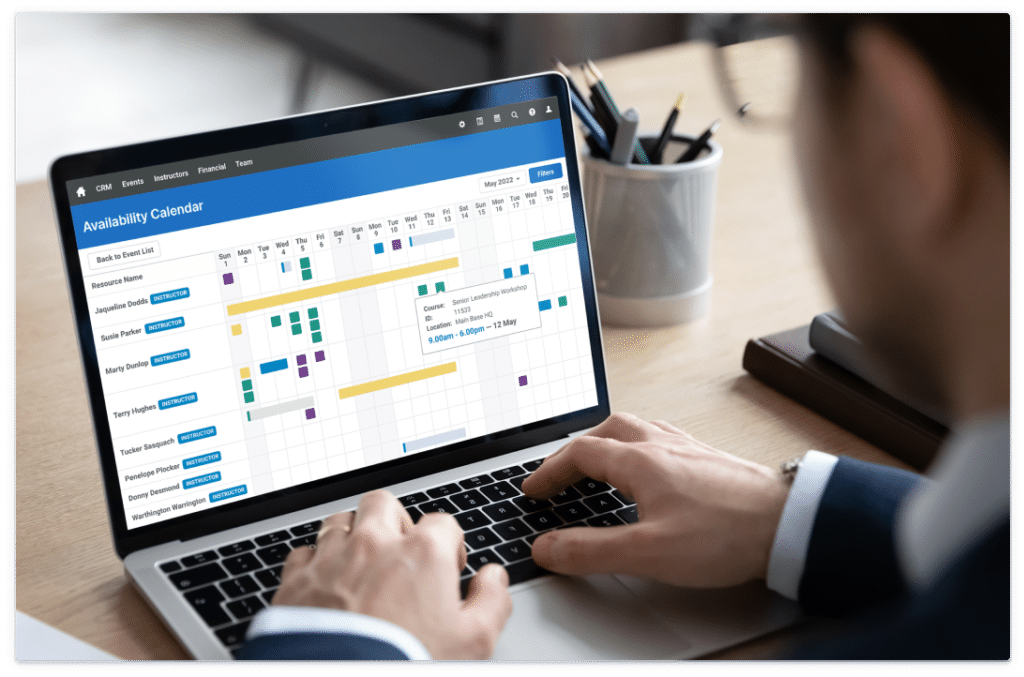
A new class of learning tech is helping training teams catch up to the data-first technologies that have transformed other functions, such as sales and marketing. A Training Management System is software infrastructure for training which acts on complex data to solve multivariate needs. A Training Management System makes it possible to:
- Forecast learning demand.
- Quickly identify resource constraints.
- Understand how specific activities create momentum in your organization and which modality works best for specific targets.
- Create agility to meet rapidly changing business needs and priorities.
- Push training insights to your organization instead of relying on pop-up demands or directives to determine program evolution.
- Leverage training as a key asset for employee engagement and retention by maximizing training time, modalities, and opportunity within resource limitations
- Easily and quickly comply with audit requirements and reporting needs
Our platform, Administrate, is a leading learning tech infrastructure for enterprise. Administrate unifies all of an organization’s existing learning tech into a single interface, sharing data and working together more efficiently to automate many training operations including many types of decision analysis.
Administrate leverages course data, learner data, training demand, and operational requirements or constraints to solve complex decisions. Here are some of the features that our clients use turn training data into organizational intelligence.How Administrate makes data-driven decisions a repeatable, scalable practice
By combining data literacy, dispelling president training data myths, and leveraging a training operations platform like Administrate, you can turn decision-making into an economy of scale.